Page 35 - Fall2011
P. 35
amino acids for optimal functioning. Further- in greater volume in mother’s milk. A sixty-five-
more, not all protein sources have equal nutri- the next question then concerns how much
tional value. protein overall do we need each day? the na- pound
tional research Council of the national Academy child requires
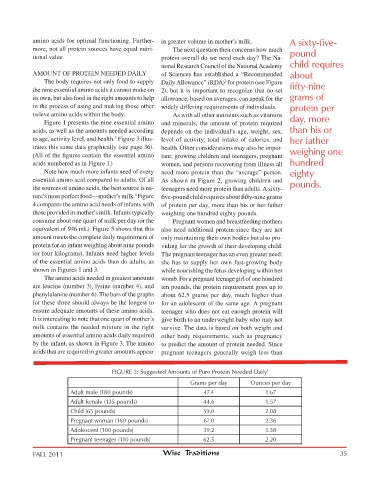
Amount oF Protein needed dAily of Sciences has established a “recommended about
the body requires not only food to supply daily Allowance” (rdA) for protein (see Figure
3
the nine essential amino acids it cannot make on 2), but it is important to recognize that no set fifty-nine
its own, but also food in the right amounts to help allowance, based on averages, can speak for the grams of
in the process of using and making those other widely differing requirements of individuals. protein per
twleve amino acids within the body. As with all other nutrients such as vitamins
Figure 1 presents the nine essential amino and minerals, the amount of protein required day, more
acids, as well as the amounts needed according depends on the individual’s age, weight, sex, than his or
to age, activity level, and health. Figure 3 illus- level of activity, total intake of calories, and her father
3
trates this same data graphically (see page 36). health. other considerations may also be impor-
(All of the figures contain the essential amino tant; growing children and teenagers, pregnant weighing one
acids numbered as in Figure 1.) women, and persons recovering from illness all hundred
note how much more infants need of every need more protein than the “average” person. eighty
essential amino acid compared to adults. of all As shown in Figure 2, growing children and
the sources of amino acids, the best source is na- teenagers need more protein than adults. A sixty- pounds.
4
ture’s most perfect food—mother’s milk. Figure five-pound child requires about fifty-nine grams
4 compares the amino acid needs of infants with of protein per day, more than his or her father
those provided in mother’s milk. infants typically weighing one hundred eighty pounds.
consume about one quart of milk per day (or the Pregnant women and breastfeeding mothers
equivalent of 946 ml). Figure 5 shows that this also need additional protein since they are not
amount meets the complete daily requirement of only maintaining their own bodies but also pro-
protein for an infant weighing about nine pounds viding for the growth of their developing child.
(or four kilograms). infants need higher levels the pregnant teenager has an even greater need:
of the essential amino acids than do adults, as she has to supply her own fast-growing body
shown in Figures 1 and 3. while nourishing the fetus developing within her
the amino acids needed in greatest amounts womb. For a pregnant teenage girl of one hundred
are leucine (number 3), lysine (number 4), and ten pounds, the protein requirement goes up to
phenylalanine (number 6). the bars of the graphs about 62.5 grams per day, much higher than
for these three should always be the longest to for an adolescent of the same age. A pregnant
ensure adequate amounts of these amino acids. teenager who does not eat enough protein will
it is interesting to note that one quart of mother’s give birth to an underweight baby who may not
milk contains the needed mixture in the right survive. the data is based on both weight and
amounts of essential amino acids daily required other body requirements, such as pregnancy
by the infant, as shown in Figure 3. the amino to predict the amount of protein needed. Since
acids that are required in greater amounts appear pregnant teenagers generally weigh less than
FIGURE 2: Suggested Amounts of Pure Protein Needed Daily 3
Grams per day Ounces per day
Adult male (180 pounds) 47.4 1.67
Adult female (135 pounds) 44.6 1.57
Child (65 pounds) 59.0 2.08
Pregnant woman (160 pounds) 67.0 2.36
Adolescent (100 pounds) 39.2 1.38
Pregnant teenager (110 pounds) 62.5 2.20
Wise Traditions FALL 2011 FALL 2011 Wise Traditions 35
82725_WAPF_Txt.indd 35 9/15/11 2:01 PM