Page 41 - Fall2011
P. 41
SubStituting Plant such as wheat and beans or soybeans would provide a sufficient supply of
for animal ProteinS essential amino acids.
much of the world population tries to meet There are three flaws in Lappe’s thinking. One is the very nature of
its need for protein with plant sources. indeed plant proteins and their manufacturing process. Processed cereals are defi-
even in the u.S., grains and cereals comprise a cient in minerals and vitamins. furthermore plant proteins are incomplete
large part of the uSDa-recommended diet for proteins and need to be eaten in combination.
protein, vitamins and minerals. the possible The second flaw is the lack of available land to grow plant proteins.
effects of moving away from animal protein to grassland that is used to graze animals cannot be converted easily into
those of plant sources should be considered. land to grow plant proteins nor should it be so converted. third, animals
in 1971, frances moore lappe published actually function very effectively to convert plants, such as grass, that
16
her book, Diet for a Small Planet, a book that people could not live on, into animal protein that people can digest.
claims to have started a revolution in the way the truth is that in terms of protein quality and calories, vegetable
americans eat. this book was revised as a proteins are not nearly the bargain they at first seem since they do not
second edition twenty years later. the book contain sufficient amounts of the essential amino acids. Plant sources of
advocated the use of cereals and legumes rather protein can be useful in a mixed diet that also includes protein from meat,
than animal protein products for the american milk and eggs, but alone, or as the major source, plant proteins fall short
diet because it assumes that cereal grains fed to for most people.
animals could be more effectively used to feed this basic difference in quality also means that it can be risky to try to
the human population. the book had an impact replace animal protein with vegetable protein substitutes, even when they
on diet recommendations of the american Heart are disguised through processing to resemble the real thing. for example,
association and the uSDa because grains and when “Egg Beaters” first came on the market, we tested them on rats.
17
legumes do not contain cholesterol and therefore rats were the best animals to use for the experiments we were conducting
are assumed to be less likely to cause heart dis- at the time. “egg beaters” were advertised as egg substitutes that were just
ease than the cholesterol in animal food products as nutritious as farm fresh eggs and even better because they contained
such as meat, cheese, and eggs. no cholesterol. We fed one group of rats on whole eggs and another on
lappe was aware that meat, cheese, and “egg beaters.” the egg-fed rats grew strong and healthy, while the rats
eggs had a greater biological value than either fed “egg beaters” became underweight and scrawny, lost their hair, and
cereals or legumes because animal food products died after only a few weeks. The “Egg Beaters” formula was deficient in an
had an essential amino acid mix that was more essential vitamin, pantothenic acid. according to the listing of ingredients
complete than the amino acid content in the pro- now on the box, that vitamin has been added and corn oil deleted from the
tein of either cereals or legumes. She reasoned original formula. the present formula, therefore, contains neither fat nor
that combinations of vegetable and grain sources cholesterol, and now has less vitamin e than the original formula. this
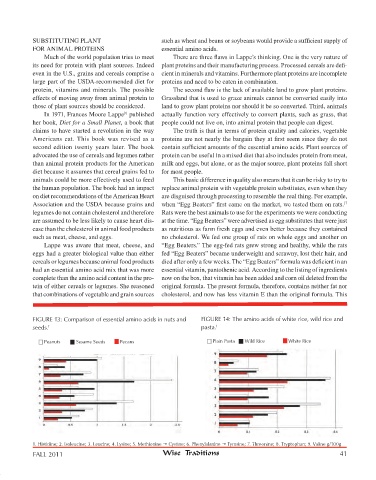
FIGURE 13: Comparison of essential amino acids in nuts and FIGURE 14: The amino acids of white rice, wild rice and
1
seeds. 1 pasta.
Peanuts Sesame Seeds Pecans Plain Pasta Wild Rice White Rice
1. Histidine; 2. Isoleucine; 3. Leucine; 4. Lysine; 5. Methionine g Cystine; 6. Phenylalanine g Tyrosine; 7. Threonine; 8. Tryptophan; 9. Valine g/100g
Wise Traditions FALL 2011 FALL 2011 Wise Traditions 41
82725_WAPF_Txt.indd 41 9/20/11 10:28 AM