Page 32 - Winter2014
P. 32
REFERENCES
1. Pew Research Internet Project, Mobile Technology
Fact Sheet, January, 2014. http://www.pewinternet.
org/fact-sheets/mobile-technology-fact-sheet/
2. FCC Consumer Guide SAR, Specific Absorp-
tion Rate For Cell Phones: What it Means for
You. March 12, 2014. http://www.fcc.gov/guides/
specific-absorption-rate-sar-cell-phones-what-it-
means-you
3. Belyaev I. Non-thermal biological effects of micro-
waves. Microwave Review, November, 2005, 13-29.
4. Behari J. Biological responses of mobile phone fre-
quency exposure. Indian Journal of Experimental
Biology, 2010, 48, 959-981.
5. World Health Organization (WHO), IARC Clas-
sifies Radiofrequency electromagnetic fields as
possibly carcinogenic to humans. Press Release,
May 31, 2011. http://www.iarc.fr/en/media-centre/
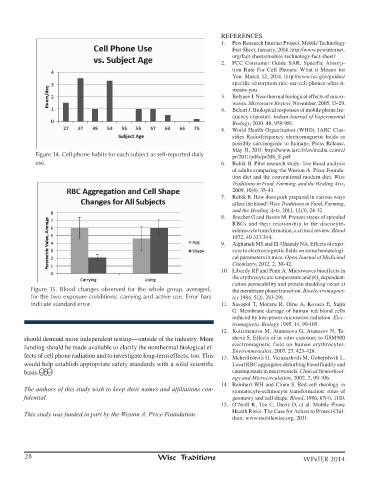
Figure 14. Cell phone habits for each subject as self-reported daily pr/2011/pdfs/pr208_E.pdf
use. 6. Rubik B. Pilot research study: live blood analysis
of adults comparing the Weston A. Price Founda-
tion diet and the conventional modern diet. Wise
Traditions in Food, Farming, and the Healing Arts,
2009, 10(4), 35-43.
7. Rubik B. How does pork prepared in various ways
affect the blood? Wise Traditions in Food, Farming,
and the Healing Arts, 2011, 12(3), 24-32.
8. Brecher G and Bessis M. Present status of spiculed
RBCs and their relationship to the discocyte-
echinocyte transformation, a critical review. Blood
1972, 40 333-344.
9. Alghamdi MS and El-Ghazaly NA. Effects of expo-
sure to electromagnetic fields on some hematologi-
cal parameters in mice. Open Journal of Medicinal
Chemistry, 2012, 2, 30-42.
10. Liburdy RP and Penn A. Microwaves bioeffects in
the erythrocyte are temperature and pO dependent:
2
cation permeability and protein shedding occur at
Figure 15. Blood changes observed for the whole group, averaged, the membrane phase transition. Bioelectromagnet-
for the two exposure conditions: carrying and active use. Error bars ics 1984, 5(2), 283-291.
indicate standard error. 11. Savopol T, Moraru R, Dinu A, Kovacs E, Sajin
G. Membrane damage of human red blood cells
induced by low-power microwave radiation. Elec-
tromagnetic Biology 1995, 14, 99-105.
12. Kouzmanova M, Atanasova G, Atanasov N, Ta-
should demand more independent testing—outside of the industry. More sheva S. Effects of in vitro exposure to GSM900
funding should be made available to clarify the nonthermal biological ef- electromagnetic field on human erythrocytes.
Environmentalist, 2007, 27, 423-428.
fects of cell phone radiation and to investigate long-term effects, too. This 13. Mchedlishvili G, Varazashvili M, Gobejishvili L.
would help establish appropriate safety standards with a solid scientific Local RBC aggregates disturbing blood fluidity and
basis. causing stasis in microvessels. Clinical Hemorheol-
ogy and Microcirculation, 2002, 2, 99-106.
14. Reinhart WH and Chien S. Red cell rheology in
The authors of this study wish to keep their names and affiliations con- stomatocyte-echinocyte transformation: roles of
fidential. geometry and cell shape. Blood, 1986, 67(4), 1110.
15. O’Neill K, Teo C, Davis D, et al. Mobile Phone
This study was funded in part by the Weston A. Price Foundation. Health Risks: The Case for Action to Protect Chil-
dren. www.mobilewise.org, 2011.
28 Wise Traditions WINTER 2014 Wise Traditions
145881_text.indd 28 12/23/14 12:16 AM